NSA就是LTE与NR的双连接,具体有:
EN-DC (4G核心网,4G基站为主站,5G基站为辅) E_UTRAN New Radio-Dual Connectivity
NE-DC (5G核心网, 5G为主,4G为辅助)
NGEN-DC (5G核心网,4G为主, 5G为辅)
用于反汇编联发科基带的ghidra nanomips isa module
原文:https://www.nccgroup.com/research-blog/ghidra-nanomips-isa-module/
原作者:James Chambers
2023年末至2024年初,NCC集团硬件和嵌入式系统业务部门承接了一项任务,对多款智能手机的基带固件进行逆向工程。这其中包括基于nanoMIPS架构的联发科5G基带固件。我们了解到一些针对Ghidra的nanoMIPS模块是私下开发的,当时并没有公开可用的可靠选项,因此我们自行开发了Ghidra的nanoMIPS反汇编器和反编译器模块。
出于(节省)时间的考虑,我们专注于实现在实际基带固件中遇到的功能和指令,而将尚不需要的复杂P-Code指令模拟保留未实现。虽然该模块仍在开发中,但它仍然能够反编译我们分析过的大部分基带固件。结合一些联发科固件中包含的调试符号信息,该模块在逆向工程过程中发挥了重要作用。
在这里,我们将演示如何将联发科基带固件用我们的 nanoMIPS ISA模块加载到 Ghidra 中,来进行分析。
为了分析固件示例,我们查找了可能搭载带5G支持的联发科SoC的手机。一些相对较新的摩托罗拉机型是不错的选择。(这些设备不属于我们的客户合作范围。)
我们在 https://mirrors.lolinet.com/firmware/lenomola/ 上找到了许多 Android 固件镜像,其中包括摩托罗拉 Moto Edge 2022(代号 Tesla)的固件镜像:
https://mirrors.lolinet.com/firmware/lenomola/tesla/official/。
该型号基于联发科 Dimensity 1050(MT6879)SoC。
固件有一些特定于运营商的版本。我们将随机选择
https://mirrors.lolinet.com/firmware/lenomola/2022/tesla/official/TMO/XT2205-1_TESLA_TMO_12_S2STS32.71-118-4-2-6-3_subsidy-TMO_UNI_RSU_QCOM_regulatory-DEFAULT_cid50_CFC.xml.zip
实际的 nanoMIPS 固件位于从ZIP包里提取的md1img.img中
为了提取md1img的文件内容,我们还编写了一些 Kaitai 结构定义,并使用简单的 Python 脚本来运行结构解析,并将不同部分输出到单独的文件中。
ksy Kaitai定义还可用于通过Kaitai IDE以交互方式探索这些文件。
使用选项–outdir 运行 md1_extract.py, 将提取其中包含的文件md1img.img:
$ ./md1_extract.py ../XT2205-1_TESLA_TMO_12_S2STS32.71-118-4-2-6-3_subsidy-TMO_UNI_RSU_QCOM_regulatory-DEFAULT_cid50_CFC/md1img.img --outdir ./md1img_out/
extracting files to: ./md1img_out
md1rom: addr=0x00000000, size=43084864
extracted to 000_md1rom
cert1md: addr=0x12345678, size=1781
extracted to 001_cert1md
cert2: addr=0x12345678, size=988
extracted to 002_cert2
md1drdi: addr=0x00000000, size=12289536
extracted to 003_md1drdi
cert1md: addr=0x12345678, size=1781
extracted to 004_cert1md
cert2: addr=0x12345678, size=988
extracted to 005_cert2
md1dsp: addr=0x00000000, size=6776460
extracted to 006_md1dsp
cert1md: addr=0x12345678, size=1781
extracted to 007_cert1md
cert2: addr=0x12345678, size=988
extracted to 008_cert2
md1_filter: addr=0xffffffff, size=300
extracted to 009_md1_filter
md1_filter_PLS_PS_ONLY: addr=0xffffffff, size=300
extracted to 010_md1_filter_PLS_PS_ONLY
md1_filter_1_Moderate: addr=0xffffffff, size=300
extracted to 011_md1_filter_1_Moderate
md1_filter_2_Standard: addr=0xffffffff, size=300
extracted to 012_md1_filter_2_Standard
md1_filter_3_Slim: addr=0xffffffff, size=300
extracted to 013_md1_filter_3_Slim
md1_filter_4_UltraSlim: addr=0xffffffff, size=300
extracted to 014_md1_filter_4_UltraSlim
md1_filter_LowPowerMonitor: addr=0xffffffff, size=300
extracted to 015_md1_filter_LowPowerMonitor
md1_emfilter: addr=0xffffffff, size=2252
extracted to 016_md1_emfilter
md1_dbginfodsp: addr=0xffffffff, size=1635062
extracted to 017_md1_dbginfodsp
md1_dbginfo: addr=0xffffffff, size=1332720
extracted to 018_md1_dbginfo
md1_mddbmeta: addr=0xffffffff, size=899538
extracted to 019_md1_mddbmeta
md1_mddbmetaodb: addr=0xffffffff, size=562654
extracted to 020_md1_mddbmetaodb
md1_mddb: addr=0xffffffff, size=12280622
extracted to 021_md1_mddb
md1_mdmlayout: addr=0xffffffff, size=8341403
extracted to 022_md1_mdmlayout
md1_file_map: addr=0xffffffff, size=889
extracted to 023_md1_file_map
最相关的文件是:
md1rom是 nanoMIPS 固件映像
md1_file_map 提供更多关于 md1_dbginfo 文件的上下文:它的原始文件名是DbgInfo_NR16.R2.MT6879.TC2.PR1.SP_LENOVO_S0MP1_K6879V1_64_MT6879_NR16_TC2_PR1_SP_V17_P38_03_24_03R_2023_05_19_22_31.xz
md1_dbginfo 是一个 XZ 压缩二进制文件,含有md1rom 的调试信息(包括符号)
提取调试符号
md1_dbginfo是包含符号、文件名以及对应的地址的另一种二进制文件格式。我们将根据md1_file_map来的文件名,对其进行重命名和解压缩:
$ cp 018_md1_dbginfo DbgInfo_NR16.R2.MT6879.TC2.PR1.SP_LENOVO_S0MP1_K6879V1_64_MT6879_NR16_TC2_PR1_SP_V17_P38_03_24_03R_2023_05_19_22_31.xz $ unxz DbgInfo_NR16.R2.MT6879.TC2.PR1.SP_LENOVO_S0MP1_K6879V1_64_MT6879_NR16_TC2_PR1_SP_V17_P38_03_24_03R_2023_05_19_22_31.xz $ hexdump DbgInfo_NR16.R2.MT6879.TC2.PR1.SP_LENOVO_S0MP1_K6879V1_64_MT6879_NR16_TC2_PR1_SP_V17_P38_03_24_03R_2023_05_19_22_31 | 头 00000000 43 41 54 49 43 54 4e 52 01 00 00 00 98 34 56 00 |CATICTNR.....4V.| 00000010 43 41 54 49 01 00 00 00 00 00 00 00 4e 52 31 36 |CATI........NR16| 00000020 2e 52 32 2e 4d 54 36 38 37 39 2e 54 43 32 2e 50 |.R2.MT6879.TC2.P| 00000030 52 31 2e 53 50 00 4d 54 36 38 37 39 5f 53 30 30 |R1.SP.MT6879_S00| 00000040 00 4d 54 36 38 37 39 5f 4e 52 31 36 2e 54 43 32 |.MT6879_NR16.TC2| 00000050 2e 50 52 31 2e 53 50 2e 56 31 37 2e 50 33 38 2e |.PR1.SP.V17.P38.| 00000060 30 33 2e 32 34 2e 30 33 52 00 32 30 32 33 2f 30 |03.24.03R.2023/0| 00000070 35 2f 31 39 20 32 32 3a 33 31 00 73 00 00 00 2b |5/19 22:31.s...+| 00000080 ed 53 00 49 4e 54 5f 56 65 63 74 6f 72 73 00 4c |.S.INT_Vectors.L| 00000090 08 00 00 54 08 00 00 62 72 6f 6d 5f 65 78 74 5f |...T...brom_ext_|
为了从调试信息文件中提取信息,我们制作了另一个 Kaitai 定义和脚本,来提取符号并以与 Ghidra 脚本ImportSymbolsScript.py兼容的文本格式输出它们:
$ ./mtk_dbg_extract.py md1img_out/DbgInfo_NR16.R2.MT6879.TC2.PR1.SP_LENOVO_S0MP1_K6879V1_64_MT6879_NR16_TC2_PR1_SP_V17_P38_03_24_03R_2023_05_19_22_31 | tee dbg_symbols.txt INT_Vectors 0x0000084c l brom_ext_main 0x00000860 l INT_SetPLL_Gen98 0x00000866 l PLL_Set_CLK_To_26M 0x000009a2 l PLL_MD_Pll_Init 0x000009da l INT_SetPLL 0x000009dc l INT_Initialize_Phase1 0x027b5c80 l INT_Initialize_Phase2 0x027b617c l init_cm 0x027b6384 l init_cm_wt 0x027b641e l ...
(目前脚本设置为仅输出标签定义而不是函数定义,因为不知道所有符号是否都用于函数。)
安装扩展
首先,我们需要为 Ghidra 安装 nanoMIPS 模块。在 Ghidra 主窗口中,前往“File > Install Extensions”,
点击“Add Extension”加号按钮,然后选择模块的 Zip 文件(例如ghidra_11.0.3_PUBLIC_20240424_nanomips.zip)。
然后重启 Ghidra。
初始加载
加载 md1rom 为原始二进制镜像(raw binary image)。
从md1img.img的解压目录中选择000_md1rom,并保留“Raw Binary”作为格式。
对于语言,点击“Browser”省略号,并使用过滤器 找到小端 32 位 nanoMIPS 选项 (nanomips:LE:32:default ),然后点击“确定”。
我们将在偏移量 0 处加载image,因此无需其他选项。再次单击“确定”即可加载原始二进制文件。
当 Ghidra 询问您是否要进行初始自动分析时,选择“否”。我们必须首先设置镜像内存地址空间0x90000000。
内存映射
打开“内存映射”窗口,然后单击“添加内存块”的加号。
我们将新块命名为“mirror”,将起始地址设置为ram:90000000,长度与基础映像“ram”块的长度(0x2916c40)匹配,权限为读取和执行,并将“块类型”设置为“字节映射”,源地址为 0,映射率为 1:1。
还要将原始“ram”块的权限更改为仅读取和执行。保存内存映射更改并关闭“内存映射”窗口。
请注意,此内存映射是不完整的;它只是使反汇编工作所需的最小设置。
调试符号
接下来,我们将加载调试符号。打开脚本管理器窗口并搜索ImportSymbolsScript.py。运行脚本并选择mtk_dbg_extract.py之前生成的文本文件 ( dbg_symbols.txt)。这将创建一堆标签,其中大部分位于镜像地址空间中。
反汇编
现在我们可以开始反汇编了。地址 0 处有一条跳转指令,可以引导我们开始,因此只需选中地址 0 处的字节,然后按“d”键或右键单击并选择“反汇编”即可。借助调试符号,您可能会注意到该指令跳转到了INT_Initialize_Phase1相应的函数。
基于流程的反汇编现在将开始发现一堆代码。初始反汇编可能需要几分钟才能完成。
然后,我们可以通过“分析 > 自动分析…”运行常规的自动分析。这应该也能发现更多代码,并需要几分钟的时间进行反汇编和反编译。
我们发现,“Non-Returning Functions”分析器在这些固件映像中使用默认配置会产生许多误报,从而扰乱代码流,因此我们建议在初始分析时禁用它。一次性“Decompiler Parameter ID”分析器是下一步运行的一个很好的选择,可以更好地检测函数输入类型。
结论
尽管该模块仍在开发中,但其结果已经可用于分析,并使我们能够对基带处理器中的一些关键功能进行逆向工程。
nanoMIPS Ghidra 模块和联发科二进制文件解包器可以在我们的 GitHub 上找到:
https://github.com/nccgroup/ghidra-nanomips
https://github.com/nccgroup/mtk_bp
小米上传安装包信息
即使是从小米应用商店下载的
com.lbe.security.miui java.net.SocketTimeoutException: failed to connect to api.sec.miui.com/192.168.0.1 (port 443) from /192.168.9.223 (port 39438) after 15000ms
微信分享如何启动指定的profile
https://android.googlesource.com/platform/frameworks/base.git/+/master/core/java/com/android/internal/app/ResolverActivity.java
com.android.internal.app.ResolverActivity的safelyStartActivityInternal
protected void safelyStartActivityInternal(
TargetInfo cti, UserHandle user, @Nullable Bundle options)
UserHandle.of(user_id)
user_id = user_handle.getIdentifier();
————-
com.miui.xspace.utils.XSpaceResolverActivityHelper
private void forward(int userId)
frida新的build方法
debian系统
1. 安装系统依赖
build-essential
git
lib32stdc++-14-dev
libc6-dev-i386
2. 安装nodejs
/etc/apt/sources.list.d/nodesource.sources
Types: deb URIs: https://deb.nodesource.com/node_23.x/ Suites: nodistro Components: main Signed-By: /usr/share/keyrings/nodesource.gpg
apt install nodejs
3. 设置环境变量
export C_INCLUDE_PATH=/usr/include/python3.13
4. 获取源代码
git clone https://github.com/frida/frida.git
5. 编译python库,脚本
./configure –prefix /home/softsim/frida
make
make install
6. 编译android64 server
mkdir build-android
export ANDROID_NDK_ROOT=/home/softsim/Android/Sdk/ndk/25.2.9519653
../frida/configure –host=android-arm64 –prefix /home/softsim/frida-android64
make
make install
7. 编译linux_x64 server
mkdir build-x64
cd build_x64
../frida/configure –host=linux-x86_64 –prefix /home/softsim/frida_x64
make
make install
Qualcomm Baseband Research
https://blog.rickmark.me/untitled/
sbl1.mbn – Secondary Bootloader (after ROM PBL)
qdsp6sw.mbn – Qualcomm Hexagon Digital Signal Processor (non-ARM core)
tz.mbn – Qualcomm TrustZone Implementation – QSEE
hyp.mbn – Qualcomm Hypervisor Execution Environment – QHEE – EL2
xbl_cfg.mbn – For XBL (eXtensible Boot Loader) or EFI based SPL signed static data
restoresbl1.mbn – Secondary program loader (bootloader) for baseband recovery
acdb.mbn – Accessory Calibration Database (seems to be initial)
apps.mbn – Userland baseband applications
rpm.mbn – Rollback prevention manager
wdt.mbn – Watchdog Timer
mba.mbn – QURT – Qualcomm Realtime OS Kernel image
MBN Signature Format
Contains a C struct styled header, followed by hashes, a signature and a certificate chain.
MBNs are ill-designed because the ELF header contains the offset to the signature region, which signs the ELF header
creating a circular dependency.
Header Region
// Likely depends on hash type - samples found stated PK algorithm scep384r1 having a signature size of 384 - deterministic noncing?
// does this lead to a potential leak of private key with double nonce values?
typedef struct {
char* hash[HASH_TYPE_SIZE]; // Unfortuantly they used all zeros to encode an empty region instead of hash of zeros...
// This seems to always be true of the signature area (b01) but also of other regions?
} mbn_hash_row_t;
typedef enum {
kSHA2_384 = 0x06;
} mbn_hash_type_t;
typedef struct {
uint32_t hash_rows; // Number of hash rows - samples with 0 have hashes but no signature... and 0xFFFFFFFF for
// pk_hash. It also has hash rows, perhaps its a problem via multiple verification paths?
mbn_hash_type_t hash_type; // 6 - SHA2-384?
uint32_t = 0
uint32_t = 0
uint32_t hash_and_signature_size; // Little endian - data following header and extra
uint32_t hash_size; // size in bytes of hash type row size * rows - signature follows
uint32_t pk_hash_one? = 0xFFFFFFFF / 0xA803708F
uint32_t signature_size; // Size of ASN.1 signature following hash list
uint32_t pk_hash_two? = 0xFFFFFFFF / 0xA803708F // Usually matches pk_hash_one
uint32_t some_size; // Some header item size or possibly align value?
uint32_t = 0;
uint32_t extra_size; // Seems to be 0x78 bytes long... 64bit extension?
char* extra[extra_size];
mbn_hash_row_t hashes[hash_rows];
} mbn_header_t;
typedef struct {
rust字节数组
array和slice的概念
数组(array)是一组拥有相同类型 T 的对象的集合,在内存中是连续存储的。数组使用中括号 [] 来创建,且它们的大小在编译时会被确定。数组的类型标记为 [T; length](T 为元素类型,length 表示数组大小)。
切片(slice)类型和数组类似,但其大小在编译时是不确定的。相反,切片是一个双字对象(two-word object),第一个字是一个指向数据的指针,第二个字是切片的长度。这个 “字” 的宽度和 usize 相同,由处理器架构决定,比如在 x86-64 平台上就是 64 位。slice 可以用来借用数组的一部分。slice 的类型标记为 &[T]。
字节数组的几种类型:
(一) [u8; N](固定大小的字节数组)
这是一个固定长度的数组,长度 N 在编译时确定。
存储在栈上(stack),如果数组过大可能导致栈溢出。
拥有数据的所有权。
大小无法在运行时改变, 如果需要改变,只能释放了再新建。
访问时可以使用 & 获取切片(&[u8])
(二) &[u8](字节切片 引用)
动态大小,存储在堆上或栈上,通常是借用(reference)。
可通过 as_ref()、deref() 或 slice::from_ref() 从数组转换。
它是一个对字节序列的不可变引用,可以指向[u8; N] 或Vec<u8> 等的一部分
不拥有数据,仅借用;长度在运行时确定。
切片本身 不拥有 任何数据。它只是指向已存在字节数据的指针和长度。数据的所有权属于切片所引用的原始数据。
切片的大小在运行时确定,由其指向的数据的长度决定。
(三) &mut [u8](可变字节切片)
和 &[u8] 类似,但允许修改数据
(四) Vec(动态字节数组)
可变长,存储在堆上(heap)。
适用于需要增长或缩短的字节数据
拥有数据的所有权,可以动态调整大小
允许 push、resize、extend 等操作。
通过 push, pop, insert, remove 等方法进行增删元素
(五) Box<[u8]>(堆分配的字节数组)
固定长度的堆分配数组,与 Vec 类似但不可变长。
适用于数据不需要增长的情况,但仍希望存储在堆上。
let boxed: Box<[u8]> = vec![1, 2, 3, 4].into_boxed_slice();
拥有所有权,在堆上分配,大小固定但可以在运行时创建
(六) Cow<[u8]>(惰性克隆的字节数组)
Cow(Copy on Write,写时复制)适用于既可能是借用的(&[u8])也可能是拥有的(Vec)数据。
适用于优化性能,避免不必要的复制,只有在需要修改时才会克隆数据。
(七) [u8] 未定大小的字节切片
这是一个抽象的字节切片类型,通常在泛型或 trait 定义中使用。
无法直接实例化,仅作为类型参数出现。
是一个视图(view)而非拥有数据的类型
(八) String和&str
用于文本字符串,以UTF-8编码的字节。本质上也是字节序列。
String拥有数据, &str是一个切片引用。
在某些情况下,你可能会将 String 或 &str 视为字节数组来处理,例如在处理 ASCII 文本或进行底层字符串操作时。但要注意,它们强制 UTF-8 编码,可能不适合处理任意二进制数据。
转换:
[u8; N] 可以转换为 &[u8] 或 &mut [u8](用 &符号 借用)
&[u8] 可以转换为 Vec( 用.to_vec()复制为Vec<u8>)
Vec 可以转换为 Box<[u8]>(比如上面的介绍的into_boxed_slice())
&[u8] 或 Vec 可以转换为 Cow<[u8]>
Vec<u8> 可以通过 .as_slice() 转为 &[u8]
&[u8] 转化 &[u8; N] , 用 try_into()
注意事项:
&[u8] 和 Box<[u8]> 是不可变的(除非使用内部可变性如 Cell 或 RefCell)
&[u8] 和 &mut [u8] 长度由引用的数据决定
sim卡引用选择文件
文件标识符(FID)用来定位和识别一个特定的文件。
同一父目录下的任何两个文件都不应具有相同的FID
当前目录的子文件或者子目录,当前目录的父目录, 当前目录的兄弟目录,这三者不能有相同的FID
短文件标识符 (SFI) 编码为 5 位,取值范围为 1 至 30。同一父级下的任何两个文件都不应具有相同的 SFI。
保留的 FID–7FFF可用作给定逻辑通道上当前活动应用程序的 ADF 的 FID。
DF除了有FID外,还可以有名字,名字就是AID, AID在每张卡上都应该唯一。 AID的长度,从1到16个字节。
——
在 UICC 激活和发送ATR给读卡器或者modem后,主文件 (MF) 被隐式选择,并成为当前目录。
(1) 通过FID应用来选择文件或者目录
选择 DF、ADF 或 MF, 都会改变当前目录, 当前EF为空,也就是不存在当前EF
选择EF, 会改变当前EF,但不会当前目录, 目录还是之前的目录,并且这个目录就是当前EF的父目录。
通过文件FID, 可以选择
[1]当前目录的直接子级的任何EF文件
[2]当前 DF 父级的直接子级的任何DF, 也就是当前目录任何兄弟DF
[3]当前目录的父级
[4]当前 DF
[5]当前活动应用的ADF
[6]MF, 也就是3F00
(2)通过 路径 来选择
路径 有3种模式:
[1] 从MF开始
[2] 从ADF开始
[3] 从当前DF开始
MF模式下,终端不得在路径开头使用 MF 的文件标识(即3F00)。
当前DF模式下,终端不得在路径开头使用特殊文件 ID–7FFF。
MF模式或者当前DF模式,终端不得使用当前 DF 的文件标识, 也不得使用空数据字段(也就空选择)。
———-
通过使用 AID 显式选择应用,就可以激活应用,并把选择的应用的 ADF 设置为当前 ADF。
当前 ADF 可以通过 FID 引用,隐式引用值为 7FFF
一个可以被选择的应用,可以通过部分DF名称模式选择,此时应该将P1 设置为 ’04’。部分选择的情况下,DF名称被右截断。
如果卡上有多个应用,它们的AID的开头的内容相同,如果采用部分DF名称模式,具体应该选择那个AID,应取决于P2值。如果P2的值表示”last”,那么选择的应该是与部分 DF 名称匹配的最后一个活动应用。
对于单应用卡,使用部分 DF 名称选择应用是可选的,但多应用卡应支持 部分DF名称选择模式。卡应该在ATR 历史字节的”卡服务数据”和”卡功能”压缩 TLV 对象中指示对此功能的支持.
如果 UICC 不支持使用部分 DF 名称进行选择,则 UICC 应以适当的响应进行响应(例如,不支持命令参数6A86)。
—————–
P1
00 通过FID选择DF, EF 或者 MF
01 选择当前DF下的子DF
03 当前DF的父DF
04 通过DF的名称(也就是AID)来选择
08 通过从MF开始的路径 来选择
09 通过从当前DF开始的路径来选择
如果 P1 = ’00’ 且数据字段为空,则应将 P2 设置为 ‘0C’(“无数据返回”)。然后,MF 被设置为当前目录。
为避免 P1 = ’00’ 时出现歧义,在选择以文件 ID (FID) 为参数的文件时,应遵循以下搜索顺序:
[1]当前 DF 的直接子文件
[2] 父 DF
[3] 父 DF 的直接子文件
当 P1 ≠ ’04’ 时,P2 的位 b2 和 b1 没有意义,应设置为 0。
当 P1 = ’04’(即通过 AID 选择)时,可以在数据字段中指定右截断 AID。
P2=04, 要求返回FCP模板
P2=0C, 不要求返回数据
rust在中国大陆的快速安装途径
之前用的是双不限流量卡,访问国外网络还比较快
换成宽带之后,访问rust网站明显变慢。
rust官方介绍的安装方法
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs | sh几乎无法安装。
改成如下命令即可
curl --proto '=https' --tlsv1.2 -sSf https://sh.rustup.rs > rust.sh
sed -i 's|static.rust-lang.org|mirrors.ustc.edu.cn/rust-static|g' rust.sh
export RUSTUP_DIST_SERVER=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/rustup
chmod a+x rust.sh
./rust.sh
安装完成后
echo "RUSTUP_DIST_SERVER=https://mirrors.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/rustup" >> ~/.cargo/env
PKI数字证书在eSIM安全上的应用研究
李宏平 孟玉明 张立星 张傲思 杜琳美
1 联通华盛通信有限公司 北京 100032
2 全国海关信息中心 北京 100005
引言
现有实体SIM卡写卡有以下两种方式:一种是通过写卡器将卡数据写入SIM卡内,此种方式SIM卡与设备是物理接触,不需要进行在线认证就能保证将卡数据写入正确的卡内;另一种是空中写卡方式,运营商通过卡内预置的号码给卡发送数据短信,将卡数据传递到卡内,SIM卡与运营商之间通过预置号码的网络参数进行认证来保证卡数据写入正确的终端内。
eSIM以密码学技术为基础,使运营商签约数据在生产、存储和递送环节与硬件分离,以电子数据的形式存在,支持通过网络远程配置到终端。在这种情况下,eSIM终端出厂前无法确认需要支持的运营商;同时也存在一个终端上可存储多个电子卡数据的情况,这些电子卡数据可能来自不同的运营商,这就会导致终端和管理平台不知道对方各自的情况。
一般来说,网络上的实体间采用数字证书的方式来进行在线的相互认证。GSMA使用PKI(Public Key Infrastructure)公钥证书体系作为eSIM安全机制的基础[1]。eSIM平台RSP(Remote SIM Provisioning,远程SIM卡数据配置)业务数字证书由eSIM CA系统签发,可作为eSIM设备和服务器在RSP业务中的身份标识,实现设备认证、服务器认证以及信息传输的完整性和抗抵赖性。
1 数字证书与eSIM安全机制
1.1 eSIM技术架构
GSMA是eSIM标准的主要研究机构,从2011年至2016年先后发布了4个版本的eUICC标准,主要面向行业物联网市场。为了将eSIM的适用范围拓展至公众消费设备,GSMA又于2016年发布了远程SIM卡数据配置(RSP)标准。RSP采用的是客户端驱动模式,适用于可穿戴、平板电脑等消费类电子产品,针对用户自签约、自配置、自管理的特点进行了优化。
为了实现eSIM的业务需求,RSP技术标准定义了一套包含管理平台、终端、eUICC、CA以及相关配套设施的技术体系[2],如图1所示。
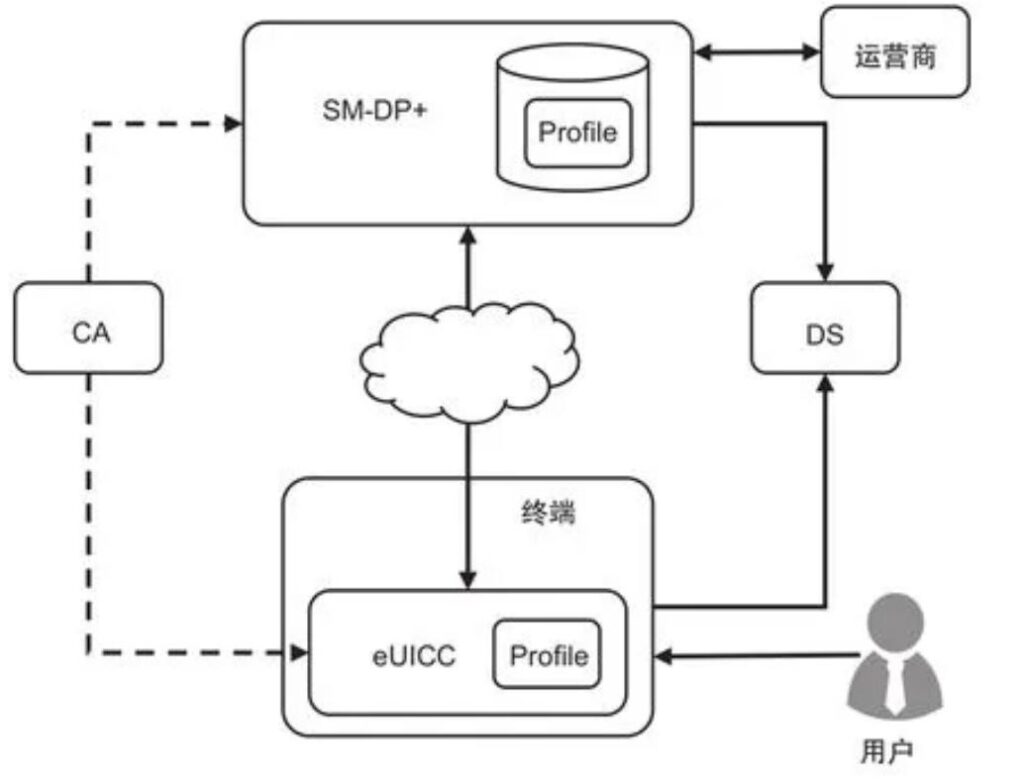
主要实体包括以下6种。
1)Profile:运营商向用户提供服务所需的卡数据和卡应用的集合,需要通过空中下载的方式安装到eUICC上。
2)eUICC:Profile的硬件载体,类似于传统USIM卡的UICC,但软硬件更复杂,可满足动态加载运营商数据的需要。同一张eUICC上可以加载属于不同运营商的多份Pro fi le,但同一时间只有一份能使用。
3)SM-DP+:负责生产、存储、提供Profile的网络服务平台。SM-DP+需具备必要的软硬件能力以确保Profile的安全。
4)终端:需要接入移动网络的实体。eUICC预置在终端中,终端也负责从SM-DP+下载Profile并写入eUICC。
5)DS:发现服务器,协助终端寻址SM-DP+。
6)CA:标准PKI证书权威机构,为体系内的通信各方颁发可信数字证书。
1.2 RSP标准的安全机制
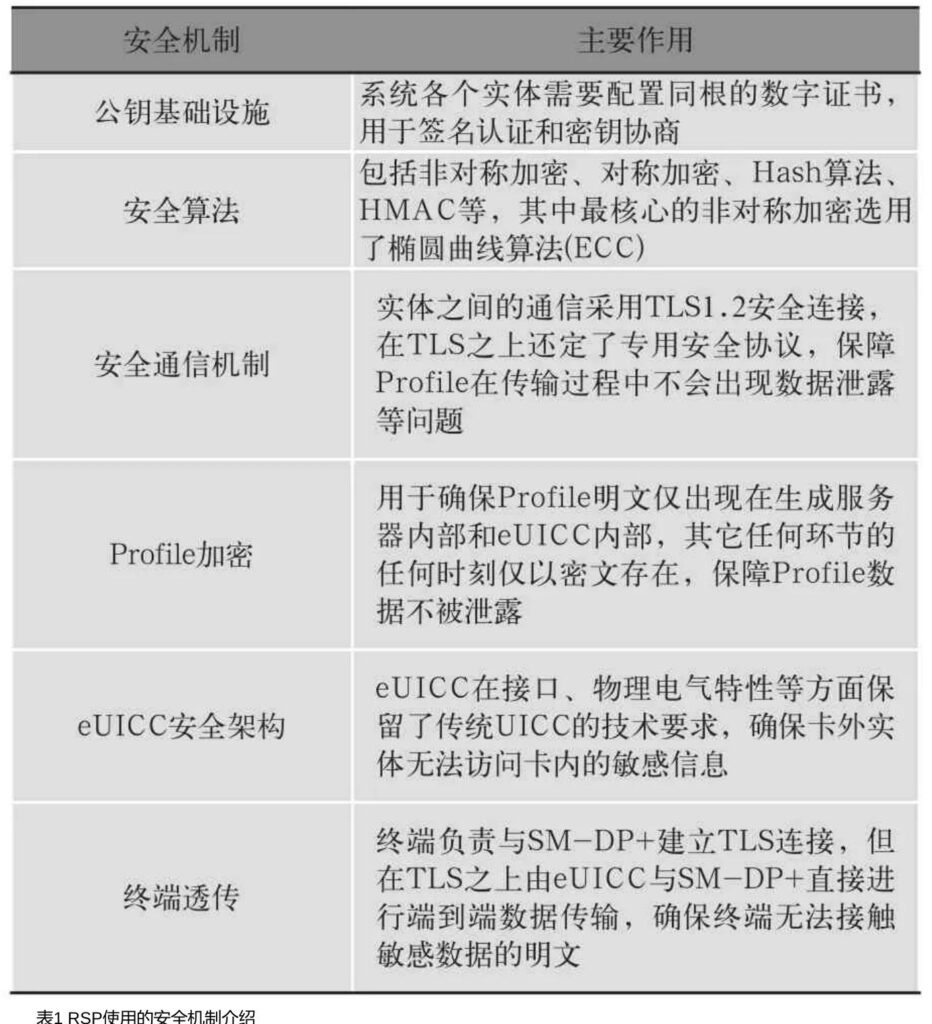
eSIM采用基于公众网络的空中写卡技术,面临Profile数据泄露、Profile被窃取等网络威胁及安全风险。GSMA RSP标准
中提供了一系列安全机制和工具,用于防止Profile在下载、存储等环节的安全威胁[3]。RSP标准要求eSIM在生产、管理、安装、使用等任何环节的安全级别不低于传统可插拔SIM卡,体系中各实体需通过GSMA定义的安全认证。在技术层面,RSP标准也定义了多种安全机制来确保安全性[4],如表1所示。
2 eSIM数字证书管理
2.1 证书分类
eSIM系统中的PKI证书体系分为三个层次:根证书、卡商证书/平台证书、eUICC证书。其中根证书是自签名证书,是信任链的起始点。EUM证书(Embedded UICC Manufacturer)也叫卡商证书,由根证书签发,eUICC证书由EUM证书签发。服务器证书也由根证书签发。RSP业务中所有的证书均为X509格式证书。
2.2 证书链
RSP标准定义的证书链如图2所示。
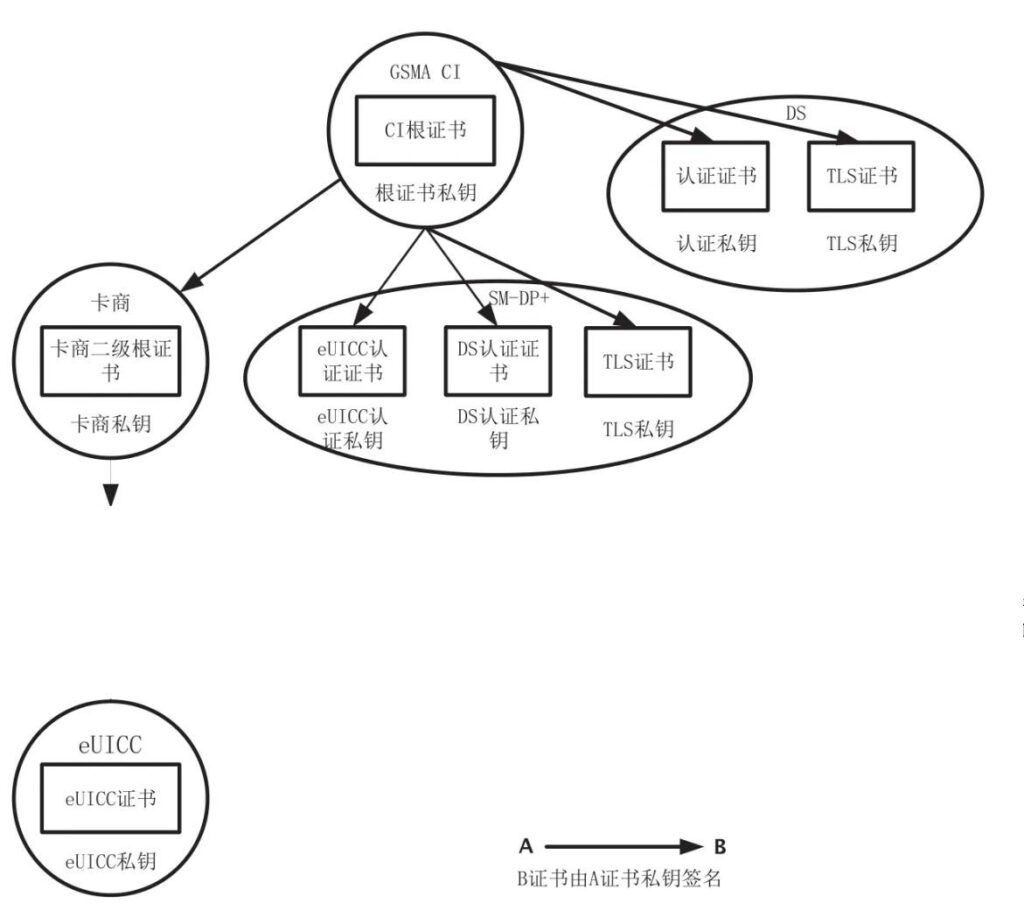
2.3 证书签发
eSIM管理系统中各个实体的证书管理需要符合PKI架构要求。CI 根证书、卡商证书、平台证书(SM-DP+证书及 SM-DP+ TLS 证书)需要由运营商认可的CI签发,但是允许SM-DP+证书与SM-DP+ TLS 证书可以由不同的CI签发。eUICC证书由卡商使用二级根证书签发,eUICC需要认证eSIM下载服务器的DP+公钥证书。
2.4 证书系统实现
eSIM CA系统由离线CA、在线CA、RA、OCSP组成[5]。离线CA是一个单独的、可信任的根CA,它生成CI根证书,并通过CI根证书签发卡商EUM证书和服务器证书。在线CA即EUM,其核心功能就是签发和管理eUICC证书,EUM具有证书发放、证书更新、证书撤销和证书验证的功能。RA (Register Authority)是面向用户的审核受理机构,负责审核终端实体的相关信息,负责维护用户的信息。通过证书中的OCSP (Online Certificate Status Protocol)服务器地址,使用在线证书状态查询服务。
证书有效性验证包括三个方面内容:
1)验证证书中的签名,确认证书是由CA签发的以及证书的内容没有被篡改;
2)检验证书的有效期,确认该证书在有效期之内;
3)查询证书状态,确认该证书没有被注销。
在进行证书验证时,逐级验证签发者直至根证书。根证书的验证通过自身公钥来验证其签名信息,CA证书验证通过根证书的公钥来验证证书的签名,用户证书验证通过相应CA证书的公钥来验证证书的签名。在验证过程中,需要判断证书是否在有效期内。
2.5 证书生命周期
证书签发下来后状态默认为有效态;当证书处于不安全状态时,可以进行冻结操作,证书状态改为冻结态,冻结态证书可以通过解冻操作恢复为有效态;有效态证书和冻结态证书均可以做吊销操作,使证书改为作废态,吊销后的证书不能改变状态。
证书的整个生命周期如图3所示[6]。
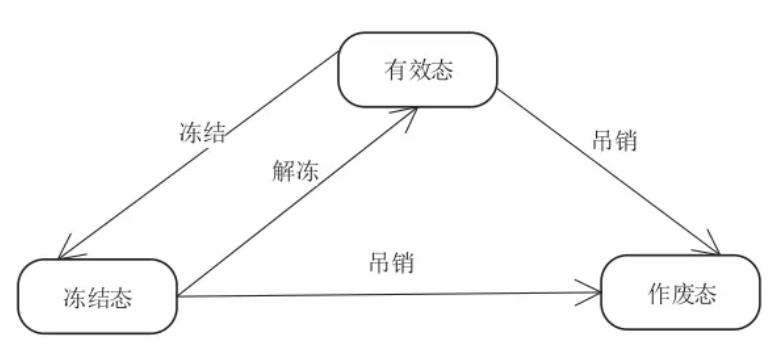
CI签发的各种证书应设置有效期,超过有效期的证书应停止使用。eSIM下载服务器会检查eUICC证书、EUM证书的有效期,超过有效期的证书将被拒绝访问。
3 数字证书在eSIM平台上的应用
eSIM管理平台的主要功能是卡数据的生成、管理以及下发。在卡数据下发之前,管理平台与RSP终端需要进行相互认证之后,才能将卡数据下发到RSP终端中的eUICC卡内。有时,RSP终端内会预置多个不同CA签发的不同根的证书,同样,管理平台也会预置多个不同CA签发的不同根的证书,在用户使用RSP终端选择运营商办理好业务之后,RSP终端可以根据运营商发来的信息访问到管理平台,通过相互认证之后管理平台将卡数据下发到RSP终端上。
管理平台与RSP终端间的相互认证过程如下:
1)当RSP终端需要进行认证时,向管理平台发送认证请求,该认证请求包括RSP终端中eSIM支持的eSIM证书的标识;
2)管理平台接收到认证请求后,在管理平台查找与eSIM证书的标识一致的DP证书,并根据认证请求中的eSIM随机数和生成的DP随机数获得DP签名体,并对DP证书和DP签名体进行签名获得DP的签名;
3)管理平台将DP证书的标识、DP证书、DP签名体和DP签名一并发送给RSP终端;
4)RSP终端接收到上述数据后,用与DP证书标识一致的eSIM证书的公钥对所述DP证书进行验证,若验证失败,则RSP终端向管理平台向发送验证失败消息,如果验证通过,则RSP终端进一步用DP证书的公钥对DP签名进行解签,并将解签后的DP签名与DP签名体进行比对,若比对一致,则RSP终端将DP随机数和eSIM的信息一起打包生成eSIM签名体,并对该eSIM签名体进行签名获得eSIM签名;
5)RSP终端向管理平台发送eSIM证书、eSIM的EUM证书、eSIM签名体和eSIM签名;
6)管理平台根据DP证书对接收到的eSIM证书和EUM证书进行验证,若验证通过,则管理平台用接收到的eSIM证书的公钥对eSIM签名进行解签,并将解签后的eSIM签名与接收到的eSIM签名体进行比对,如果比对一致,则认证成功完成本次认证。
其中,进行签名的步骤可以由管理平台自身进行签名,也可以单独授权给独立的模块进行签名。例如单独设置加密机,管理平台将需要进行签名的数据发给加密机进行签名,并获得加密机返回的签名。如果RSP终端的eSIM支持多个eSIM证书,则针对每个eSIM证书都按照上述流程提供的认证方法进行认证,从而实现RSP终端的多运营商支持功能。
4 多证书管理现状及发展趋势
4.1 多证书
选择合适的证书服务是保障运营商数据安全的关键。eSIM证书服务既要符合GSMA标准,又需满足政府监管要求,目前国际上提供证书服务的主要两家:CyberTrust、Symantec。GSMA特别准许国内运营商自己选择CI,CA证书签发者必须是工业与信息化部公布的具有电子认证服务行政许可的认证机构,目前,三家运营商各自有CA,国内的电信终端产业协会(TAF)也是具备为eSIM平台及EUM颁发证书的CA。
RSP标准基于PKI的信任机制允许eUICC同时访问多个eSIM管理平台,理论上eUICC上只需要安装一张证书就可以,但这只是理想状态。例如美国Verizon和AT&T互不使用对方的证书。为了解决这个问题,RSP标准定义了多证书机制,eUICC中可以同时安装多张CA证书,按需使用。eUICC应能支持多个根证书,eSIM下载服务器也应能支持多个根证书,并能根据eUICC支持根证书的情况选择合适的证书。
4.2 GSMA统一根证书策略分析
为了实现全球互通,GSMA希望根证书统一由经过认证的CA签发,但为了满足各国政府监管需要,GSMA在SGP.28规范定义了两种CI:GSMA Root CI和Independent Root CI。
根据GSMA 规范要求,CI选择需要考虑的因素包括:
1)公司制度完善;
2)有能力对申请证书的企业的资质进行验证;
3)有能力保护整个生态体系;
4)积极参与eSIM发展;
5)能证明产品质量;
6)具备CI领域的知名度;
7) 产品覆盖广度(建议至少被8个运营商支持);
8)产品覆盖的区域(建议至少在2个以上区域使用);
9)具备长期服务的能力;
10)符合技术规范;
11)对各厂商中立无歧视;
12)签发证书的效率。
根据国内运营商发展现状,国内运营商提出针对GSMA的部分条件应当允许适当调整,如:为保证尊重运营商平等选择权利,只要有一家运营商推荐即可申请成为CI;对CI申请评估应该注重技术性因素,综合考虑市场规模因素,而不是运营商个数;覆盖多少国家、有多少运营商支持不应成为对CI的准入要求;签发证书的历史长短不应成为对CI的准入要求等条件。同时,为解决全球互通,减少eUICC需要安装的CA数量,降低DP+平台安装多个CA所需的成本,GSMA需要提供一个完整的CI解决方案,在该方案中应该体现如下原则:
1)多个CI组成CI包(CI Package) ,以实现对多个监管地区的覆盖;
2)对于每个监管地区,都需要有至少1个被该地区法律认可的CI在包中;
3)DP+需支持包中的所有被其所在地区认可的CI(不能选择性支持),eUICC则只需选择其中一个CI(需要支持跨区域时需每个区域选择一个CI);
4)建议GSMA在认证CI时一并解决CI的商务问题,DP+平台可以合理的价格获得并安装该监管地区内所有CI颁发的证书。
4.3 国内CA管理策略研究
由于国内运营商的eSIM平台均采用自建的技术路线,在证书服务选择上,终端厂商及卡商的话语权较弱,国家相关管理机构也未明确政策意见,因此目前仍由运营商自主选择为主。同时,中国三家运营商互不使用对方证书,这导致终端eUICC需预置多家证书,提升了终端复杂度,也不符合GSMA对统一根证书的管理原则。
国内CA管理需要一套互联互通方案,在设计时应考虑符合中国法律和监管要求、保证终端可以与各家运营商的DP/DP+互通、eUICC上只需安装一个CA就可以连接全部运营商的DP/DP+、需要具备商业上的公平性、合理性和可行性。基于此,我们提出如下三种可行方案。表2对三种方案做出了比较。
| CI方案 | 优点 | 缺点 |
| 公益性单CI | 监管简单,只需要管理一家CI; 产业链成本低; 对各厂家相对公平 | 缺少商业驱动,服务质量不能保证; 对新技术新业务不能提供很好的支持 |
| 运营商互认多CI | eUIIC侧 通过市场公平选择; 运营商背书保证CI服务质量; 对CI的管理与对运营商的管理合二为一 | 平台需支持多CI |
| 市场化多CI | 通过市场公平选择; 通过竞争,CI服务质量较有保证 | 平台需要支持多CI,管理相对复杂; 实力差的企业可能因市场变化无法提供长期的技术支撑 |
4.3.1 公益性单CI方案
由监管部门指定一个CI作为统一CI,该CI需要是公益事业性质,由政府提供资金支持,不对运营商(平台证书,包括TLS证书)、eUICC厂商(EUM证书)收取费用。
4.3.2 运营商互认多CI方案
1)由监管部门组织统一CI入围招标,入围厂家数量可控制在3家左右。
2)平台证书免费。所有CI无歧视地向个运营商签发平台证书,所有运营商需要无歧视地支持各个CI的证书。
3)eUICC只需要安装一个CI的证书,由eUICC厂家自主选择用哪个CI,eUICC厂家与CI厂家自主进行商务谈判。
4.3.3 市场化多CI方案
1)由监管部门组织统一CI入围招标,入围厂家数量可控制在3~4家左右。
2)平台证书免费。所有CI无歧视地向个运营商签发平台证书,所有运营商需要无歧视地支持各个CI的证书。
3)eUICC只需要安装一个CI的证书(但不限制安装数量),由eUICC厂家自主选择用哪个CI,eUICC厂家与CI厂家自主进行商务谈判。
5 结语
eSIM是对移动通信技术的一次重大改进,使通信服务摆脱了SIM卡线下发卡环节的束缚,可实现全面互联网化的业务流程,让用户获得随需、即时入网的极致体验。终端商则得以摆脱卡槽束缚,优化产品外观并提升性能,如减小体积、增加电池续航、增强防水能力等,为广大消费者带来更多、更好的产品。
随着智能手表等可穿戴设备在国内的普及,eSIM技术在移动通信业务中扮演的角色越来越重要,其安全性问题深受产业链各方的关注。eSIM采用基于公众网络的空中写卡技术,为解决Pofile在传输过程中的安全性,采用了一套基于PKI的同根数字证书作为eSIM设备和服务器的身份标识。目前国内各运营商已确定使用自建的eSIM平台进行业务发展,对eSIM平台上的数字证书应用与管理必将引起更多重视,数字证书颁发机构之间的互相认可也将成为值得研究的新课题。